Wearable Tech: Will Health Monitoring Devices Become Essential by 2025?
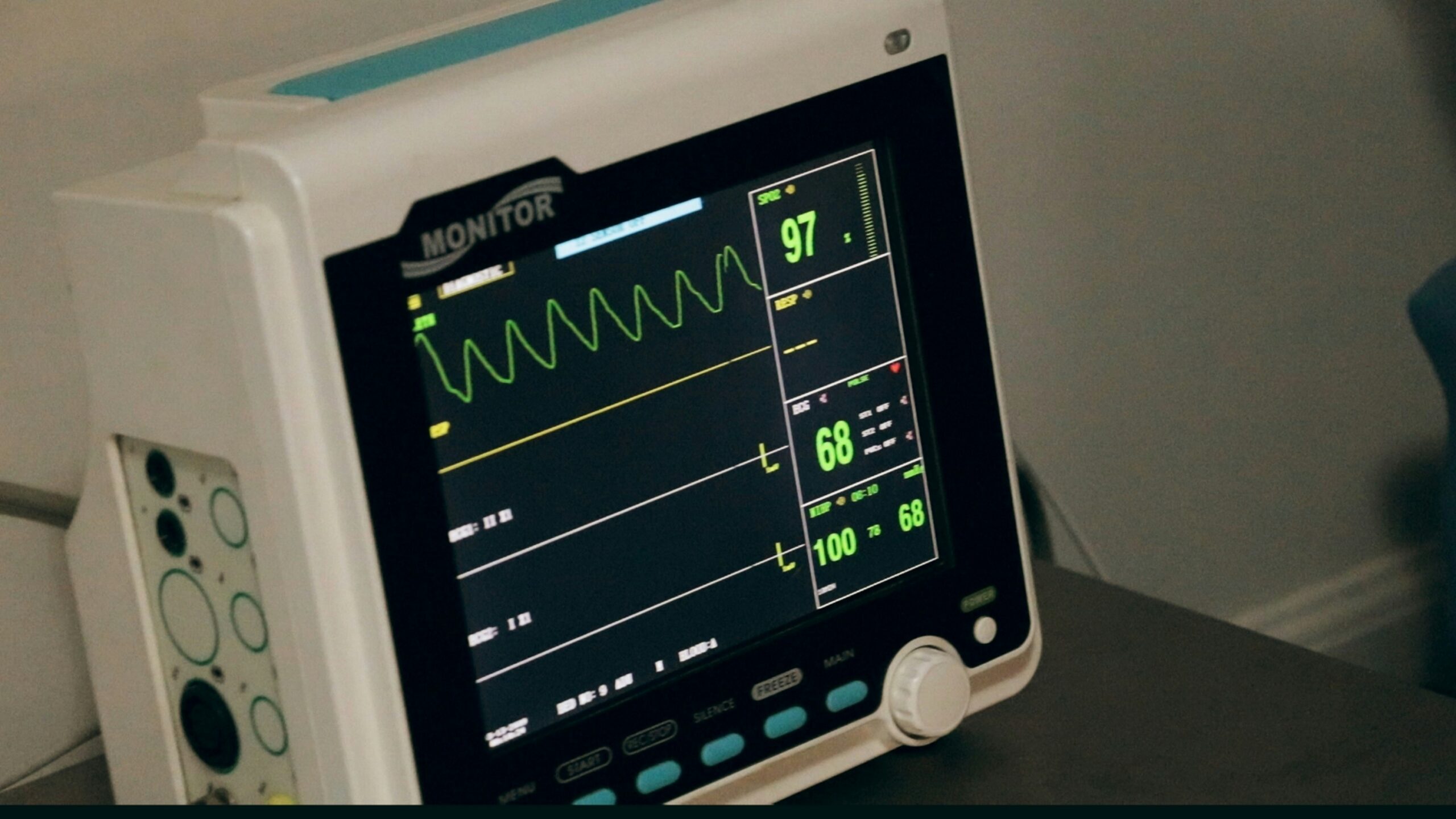 Photo by Jair Lázaro on Unsplash
Photo by Jair Lázaro on Unsplash Introduction to Wearable Technology
Wearable technology has experienced significant evolution over the past decade, transforming from basic activity trackers to sophisticated health monitoring devices. This shift highlights a growing interest in personal health tracking, as consumers seek to take control of their well-being through innovative technology. Various types of wearable devices are currently available, ranging from smartwatches and fitness bands to advanced health monitors equipped with sensors that provide real-time data.
In recent years, the emergence of smartwatches has contributed notably to the popularity of wearable technology. These devices not only display time and notifications but also include features for tracking heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activities. Moreover, contemporary fitness bands are designed to monitor various metrics like steps taken, calories burned, and even stress levels, making them an essential accessory for fitness enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals alike.
In addition to smartwatches and fitness bands, there are more specialized health monitoring devices that have gained attention. These include continuous glucose monitors for individuals with diabetes, ECG monitors that detect abnormal heart rhythms, and wearable blood pressure cuffs. The integration of advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms has enhanced the accuracy and reliability of these devices, providing users with invaluable insights into their health status.
Current trends in wearable technology indicate a move toward greater connectivity and user engagement. The ability to sync these devices with smartphones and health applications allows users to compile their health data conveniently, enabling comprehensive monitoring and personalized health management. As society becomes increasingly health-conscious, the demand for wearable technology is likely to rise, setting the stage for a future where such devices may be deemed essential for maintaining optimal health and wellness.
Current Capabilities of Health Monitoring Devices
Health monitoring devices have evolved significantly over the years, becoming essential tools for individuals seeking to manage their well-being. Today’s landscape of wearable technology includes an array of devices such as heart rate monitors, fitness trackers, sleep trackers, and smartwatches, each designed to track various aspects of health. These devices primarily function by utilizing sensors and algorithms that can provide real-time data to users.
Heart rate monitors, for instance, are now widely integrated into many fitness trackers and smartwatches. They utilize photoplethysmography (PPG) technology to detect the pulse rate by measuring blood flow through the skin. This feature not only assists athletes in optimizing their workouts but also aids in monitoring cardiovascular health, making it advantageous for users seeking preventative care.
Fitness trackers go beyond heart rate monitoring, often including additional features like step counting, calorie tracking, and workout recognition. These devices can motivate users to achieve personal fitness goals while promoting a more active lifestyle. Advanced models also utilize GPS technology to track outdoor activities and provide insights into distance covered and route efficiency.
Sleep trackers have gained popularity, providing users with an understanding of their sleep patterns and quality. Many of these devices analyze data such as time spent in different sleep stages and disturbances during the night. This information can be invaluable for individuals struggling with sleep-related issues, enabling them to take steps towards improving their rest.
Smartwatches often combine the functionalities of heart rate monitors and fitness trackers with additional perks like notifications, apps, and mobile payments. They not only collect health data but also integrate seamlessly with smartphones, enhancing user experience by providing a hub for health management.
In terms of accuracy and reliability, most modern health monitoring devices are equipped with sophisticated algorithms that have been validated through clinical trials. These advancements ensure that the data provided is both consistent and actionable, enabling users to make informed health decisions.
The Role of Data in Health Management
In the rapidly evolving landscape of wearable technology, the role of data collected by health monitoring devices has gained substantial importance in both personal and professional health management. These devices, ranging from smartwatches to specialized fitness trackers, are capable of gathering a vast array of data points, including heart rates, activity levels, sleep patterns, and even blood oxygen saturation. This wealth of information serves as a foundation for making informed decisions regarding health and wellness.
Healthcare providers leverage the data collected from these wearable devices to enhance patient care. By analyzing trends and anomalies in a patient’s health data over time, practitioners can identify potential health issues before they escalate. For instance, consistent monitoring of heart rate variability may reveal underlying cardiovascular problems, prompting timely interventions. This proactive approach shifts the focus from reactive healthcare to preventive care, reducing the burden on healthcare systems and improving overall health outcomes.
For individuals, the ability to monitor personal health metrics empowers them to take charge of their wellness. Armed with real-time insights into their physical activity and health status, users can tailor their lifestyle choices to meet their health goals. This data enables users to set realistic fitness targets, track progress, and make necessary adjustments to their routines, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into data analysis enhances the utility of the information collected by health monitoring devices. These technologies can provide predictive analytics, helping users anticipate potential health risks based on their data patterns. As we approach 2025, it is evident that the utilization of data from wearable tech will play a crucial role in shaping personalized healthcare strategies and promoting preventive measures among individuals and healthcare providers alike.
Market Trends and Consumer Demand
The landscape of wearable technology, particularly health monitoring devices, is witnessing a significant transformation. As of 2023, data indicates a robust adoption rate, with over 30% of adults in developed countries utilizing these devices regularly. This surge can be primarily attributed to an increased awareness of personal health and wellness, coupled with advancements in technology that have made these devices more accessible and user-friendly.
Demographically, younger consumers, especially millennials and Generation Z, are leading the way in adopting health monitoring technology. Approximately 50% of individuals aged 18-34 report using fitness trackers or smartwatches to manage their health metrics such as heart rate and activity levels. On the other hand, older adults are increasingly embracing these technologies as well, primarily for chronic disease management and health tracking, indicating that the market is broadening its appeal across age groups. This expanding consumer base suggests a promising future for health monitoring devices.
Marketing efforts have played a pivotal role in shaping consumer behavior towards these products. Campaigns leveraging social media influencers and testimonials have proven particularly effective, as consumers often seek validation from peers before making purchasing decisions. Furthermore, significant investments by tech companies in research and development have not only improved device functionalities but also enhanced overall user experience, contributing to rising demand. As brands establish credibility and foster trust among consumers, the likelihood of health monitoring devices becoming essential by 2025 increases. These trends reflect a genuine shift in consumer priorities, wherein health management is taking center stage in everyday life, reshaping demand for wearable technology.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
As the adoption of wearable health technology continues to grow, several challenges and limitations must be addressed to ensure its success. One of the primary concerns relates to data privacy. Wearable devices collect vast amounts of sensitive personal health information, which raises questions about how this data is stored, shared, and utilized. Users may be hesitant to fully embrace these technologies if they fear their information may be compromised or misused. Striking a balance between functionality and safeguarding user privacy remains a significant hurdle for developers and manufacturers in the wearable tech industry.
Another critical consideration is the accuracy of health monitoring devices. Although technology has advanced considerably, issues still arise regarding the precision of the data collected. For instance, discrepancies in heart rate measurements or inaccuracies in sleep tracking can lead to misinterpretations of a user’s health status. As a result, potential users may be skeptical about relying on these devices for health monitoring. Continuous advancements in sensor technology and data analytics are essential to improving accuracy and building user trust in wearable devices.
Moreover, the digital divide presents additional barriers to widespread acceptance of wearable health technology. Accessibility is an ongoing issue, as individuals from low-income backgrounds or those residing in rural areas may lack access to the latest devices or the necessary infrastructure to use them effectively. This disparity can result in unequal health monitoring capabilities, furthering the gap in health outcomes across different demographics. Addressing these inequities will be crucial to integrating wearable technology into everyday life, ensuring that all individuals can harness the benefits of health monitoring devices.
Future Innovations in Wearable Health Tech
The landscape of wearable health technology is poised for significant transformation by the year 2025, presenting an array of innovative advancements that promise to reshape user engagement and health insights. One of the prominent trends anticipated is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) within wearable devices. This incorporation is expected to enhance data analysis capabilities, allowing devices to provide personalized health recommendations based on individual lifestyle patterns and biometrics. Rather than simply tracking health metrics, future wearables could evolve into intelligent health companions that learn and adapt to user needs over time.
Advancements in sensor technology are another crucial area to watch. Researchers are continuously working on developing more sophisticated sensors that could monitor a broader range of health parameters with increased accuracy. For instance, potential innovations may include sensors that can detect early signs of chronic conditions or even monitor biochemical markers in sweat. Such developments would not only improve the comprehensiveness of health data collected but also facilitate early interventions, thus enhancing overall health management.
Moreover, user engagement features are likely to become more robust and interactive. Wearable health tech may incorporate gamification elements, enabling users to set health goals and achieve them through engaging activities and challenges. Furthermore, real-time health monitoring functionalities could be expanded, allowing for timely notifications and alerts that encourage individuals to take preventive actions, thereby fostering a proactive approach to health care. All these advancements, driven by a growing emphasis on health and wellness, could lead to a significant evolution of health monitoring devices, making them increasingly essential to daily living by 2025.
Healthcare Integration and Regulatory Landscape
As the prevalence of wearable health monitoring devices continues to rise, their integration into the healthcare system is becoming increasingly essential. These devices, which range from fitness trackers to sophisticated medical-grade monitors, are being embraced by healthcare providers for their potential to enhance patient care and streamline clinical processes. As technology companies develop innovative solutions, many are forming strategic partnerships with healthcare organizations to promote the use of wearable technologies. Such collaborations aim to harness data collected from these devices to uncover insights that drive preventative care and real-time health monitoring.
The role of wearable devices in healthcare is evolving as they facilitate remote patient monitoring and chronic disease management. This transformation is particularly significant for managing conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, where timely data can inform treatment decisions and enhance patient adherence. However, the integration of wearables into existing healthcare frameworks is not without challenges, especially concerning regulatory compliance and patient privacy. To mitigate these issues, governing bodies are implementing regulations that ensure the safety, efficacy, and reliability of wearable health technologies.
While various countries have taken the initiative to introduce specific guidelines for wearable devices, such as the FDA’s regulatory framework in the United States, ongoing discourse about the standardization of these measures continues. Regulators are tasked with balancing innovation and consumer safety, ensuring that devices operate within predetermined efficacy parameters and that user data remains secure. As we move closer to 2025, it is anticipated that these regulatory landscapes will evolve to accommodate the growing intersection of technology and healthcare, establishing clear pathways for device approval and use in clinical settings.
In closing, the future of wearable health monitoring devices hinges on their seamless integration into healthcare systems, bolstered by robust regulatory measures that prioritize both safety and functionality. As partnerships between tech companies and health providers strengthen, the momentum for widespread adoption will likely increase significantly.
Expert Opinions and Predictions
The landscape of health monitoring devices is experiencing rapid transformation, with many experts projecting that these technological advancements will become essential to everyday life by 2025. Healthcare professionals and market analysts alike agree that the integration of wearable technology into personal health management will be driven by a combination of fields including medicine, engineering, and consumer electronics.
One prominent viewpoint from industry analysts suggests that the increasing prevalence of chronic conditions will bolster the demand for continuous health monitoring devices. As more individuals seek proactive ways to manage their health conditions—such as diabetes and hypertension—the value of real-time data provided by wearables will become indispensable. For instance, devices that offer features such as heart rate monitoring, sleep tracking, and blood glucose management may significantly enhance patient outcomes by allowing for timely interventions.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on preventative healthcare is anticipated to foster a culture that prioritizes health awareness and maintenance. Experts predict that as people become more health-conscious, the adoption rate of these devices will surge. Additionally, advancements in data analytics and artificial intelligence can provide personalized health tips based on the data collected, making wearables even more relevant in daily life. The shift toward telehealth services further strengthens this predicted trend; remote monitoring capabilities offered by health devices facilitate ongoing patient-provider interactions, thus enhancing the healthcare experience.
Despite varying opinions regarding the timeline, consensus is building on the likelihood that by 2025, health monitoring devices will not merely be optional; rather, they will be integral tools for promoting and managing health. The convergence of technology, healthcare systems, and consumer demand will undoubtedly shape the future landscape of wearable technology, making them essential for a proactive approach to health management.
Conclusion: The Future of Wearable Health Monitoring Devices
As we reflect on the rapid advancements in wearable technology, it becomes evident that health monitoring devices are poised to play an increasingly significant role in our lives. The integration of these devices into everyday routines symbolizes a shift towards a more proactive and personalized approach to health management. Over the past few years, the development of sophisticated sensors and devices has enhanced the capability of users to track a variety of health metrics, including heart rate, sleep patterns, and overall fitness. This shift empowers individuals to take charge of their health in ways that were previously unimaginable.
The evidence presented throughout this discussion indicates that the trend towards wearable health monitoring devices will continue to grow significantly by 2025. Factors such as heightened consumer awareness regarding personal health, an aging population, and advancements in technology will drive the adoption of these devices. Not only do they provide real-time feedback, but they also facilitate better communication between patients and healthcare providers, allowing for more informed healthcare decisions. As more individuals become accustomed to using wearable devices, their perceived value is likely to increase, leading to widespread acceptance.
Furthermore, the potential benefits of health monitoring devices extend beyond individual users. Healthcare systems may experience increased efficiency with the data gathered from these devices, which can inform public health initiatives and resource allocation. Thus, the implications of wearables could transform not just personal health management, but also the healthcare landscape as a whole.
Ultimately, consumers are encouraged to explore the available technology tailored to health monitoring. The insights gained through these devices can foster better health outcomes and empower users to live healthier lifestyles. With that in mind, it is reasonable to conclude that health monitoring devices will likely become essential tools for managing health by 2025, offering substantial advantages for both individuals and the healthcare industry at large.



No Comments